Eczema: Types and Treatments
Eczema is a group of chronic inflammatory skin conditions believed to be caused by a genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. Symptoms of this condition typically present on the skin’s outermost layer, known as the epidermis, and they can emerge in infancy or early childhood. As a relatively common condition, more than 31 million Americans suffer from some type of eczema.
Types of Eczema
There are several kinds of eczema that may develop and each type has its own set of triggers. Seven of the most common types of eczema include:
Atopic Dermatitis
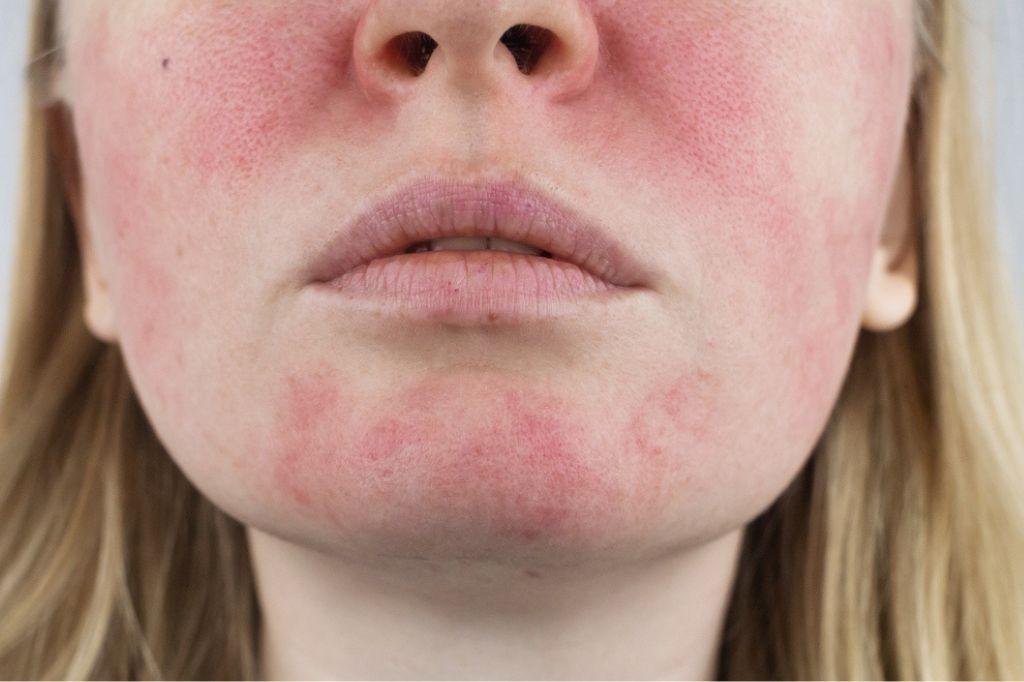
Atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema, presenting as itchiness, discoloration, dryness, and scaling. This type of eczema may cause rashes that appear red on lighter skin tones and purple, brown, or gray on darker skin tones. Repetitive scratching of atopic dermatitis can also cause the skin to thicken and harden, a process known as lichenification. Flare-ups are most frequently seen on the face, hands, elbows, knees, feet, and behind the ears.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a condition that occurs when the skin makes direct contact with an irritant or allergen that triggers a reaction. There are two main types of contact dermatitis:
- Irritant contact dermatitis: does not involve an allergic reaction but happens when skin cells become exposed to an external irritant, which damages the skin.
- Allergic contact dermatitis: when an allergic reaction occurs as a result of exposure to an allergen.
The exposure usually causes itching, burning, swelling, or blistering sensation on the skin. This type of eczema is most common in people whose professions involve the use of chemicals.
Dyshidrotic Eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema is a condition that causes small, intensely itchy, fluid-filled blisters called vesicles to form on the hands and feet. Found more frequently in women and young adults, dyshidrotic eczema can be triggered by stress, sweating, and exposure to metals.
Neurodermatitis
Neurodermatitis is a type of eczema that is localized to one area of the body and is characterized by severe itching. These patches of skin tend to flare up when affected individuals are trying to relax or when they feel stressed or anxious. Over time, excessive scratching can lead to:
- Lichenification
- Scarring
- Bleeding wounds
- Infection
- Scabbing
- Hair loss
Nummular Eczema
Nummular eczema presents itself as round lesions on the skin. These lesions are often red, dry, and itchy, leading to significant skin damage if left untreated. Sometimes the lesions have an oozing liquid or are surrounded by inflamed skin. Unlike other types of eczema, nummular lesions rarely improve without treatment.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a skin condition that is likely caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia, a yeast that is present on the skin’s surface. This condition typically affects areas of the body that are covered with hair, including the following:
- Scalp
- Nose
- Eyebrows
- Mid-chest
- Upper back
- Armpits
- Groin area
It typically appears as small, scaly patches on the skin’s surface that are mildly itchy and can also present as stubborn dandruff.
Stasis Dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis is a form of eczema that occurs in people who have a history of venous insufficiency, which is a condition that causes blood to pool in the veins. This stagnation of blood can cause:
- Itchy and dry skin
- Irritated and discolored skin
- Heaviness or aching in your legs
- Swelling in your lower legs
Eczema Treatments
There are a variety of treatment methods for eczema, depending on:
- Severity of symptoms
- Underlying medical conditions
- Type of eczema
Some of the most common treatments include:
- Topical corticosteroids
- Phototherapy
- Systemic corticosteroids
- Dietary and lifestyle modifications
- Prescription injectables
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Vitamins and supplements
- Antihistamines
For at-home care, the providers at Academic Alliance in Dermatology (AAD) recommend:
- Moisturizing every day
- Using a humidifier in cold and dry weather
- Wearing soft fabrics
- Bathing in lukewarm (not hot) water
- Using gentle cleansers that are unscented, fragrance-free, and dye-free
Visit Academic Alliance in Dermatology
At AAD, we understand the significant impact eczema can have on your quality of life, which is why our providers’ top priority is getting you the care you need. If you would like to find out more about the dermatological services that we offer or learn more about your inflammatory skin condition, contact us today.